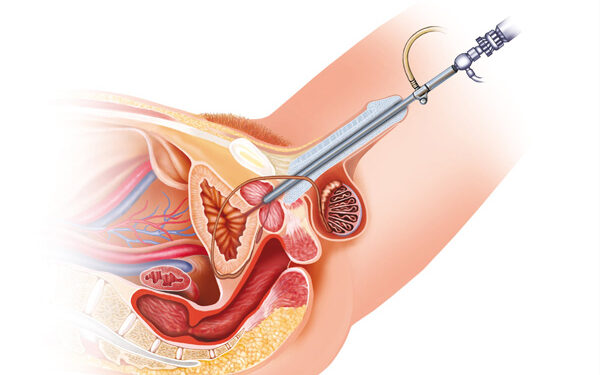
A urethral (u-REE-thru) stricture involves scarring that narrows the tube that carries urine out of your body (urethra). A stricture restricts the flow of urine from the bladder and can cause a variety of medical problems in the urinary tract, including inflammation or infection.
Urethral stricture refers to the buildup of scar tissue in the urethra, which is the passage that empties urine from the bladder, slowing or blocking the ability to urinate. Men have a longer urethra and are more likely to experience scarring or narrowing of their urethra than women and infants.
The average male urethra, which runs from the bladder to the tip of the penis, is about 20 centimeters or approximately 8 inches in length and is surrounded by vascular tissue known as the corpus spongiosum. Stricture or narrowing can occur at any point in the urethra and is categorized based on where it occurs along the urethra.